 This website is best viewed
This website is best viewed
using the horizontal display on
your tablet device.
Healthcare Professionals only.
ENGLISH
FRANÇAIS
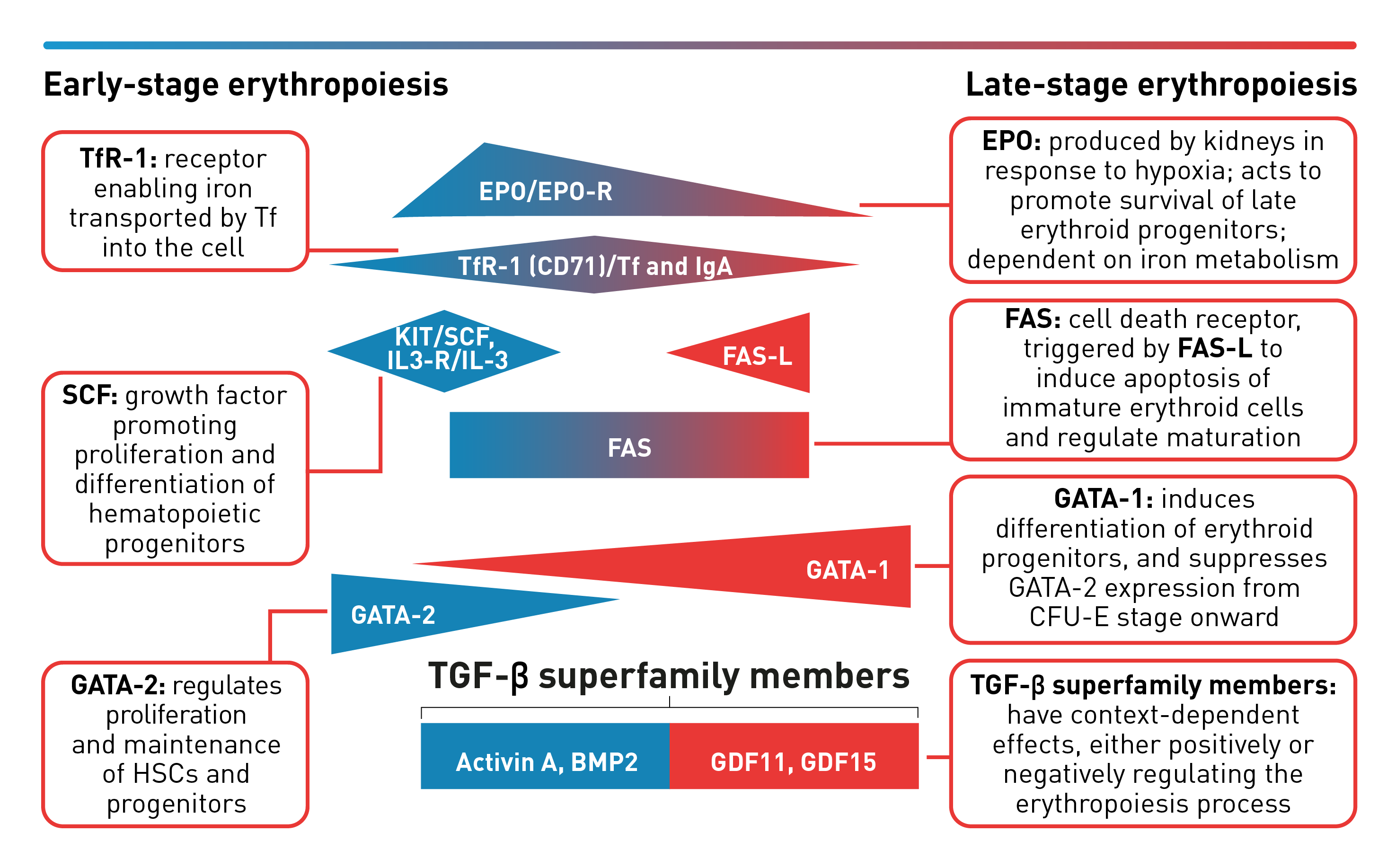
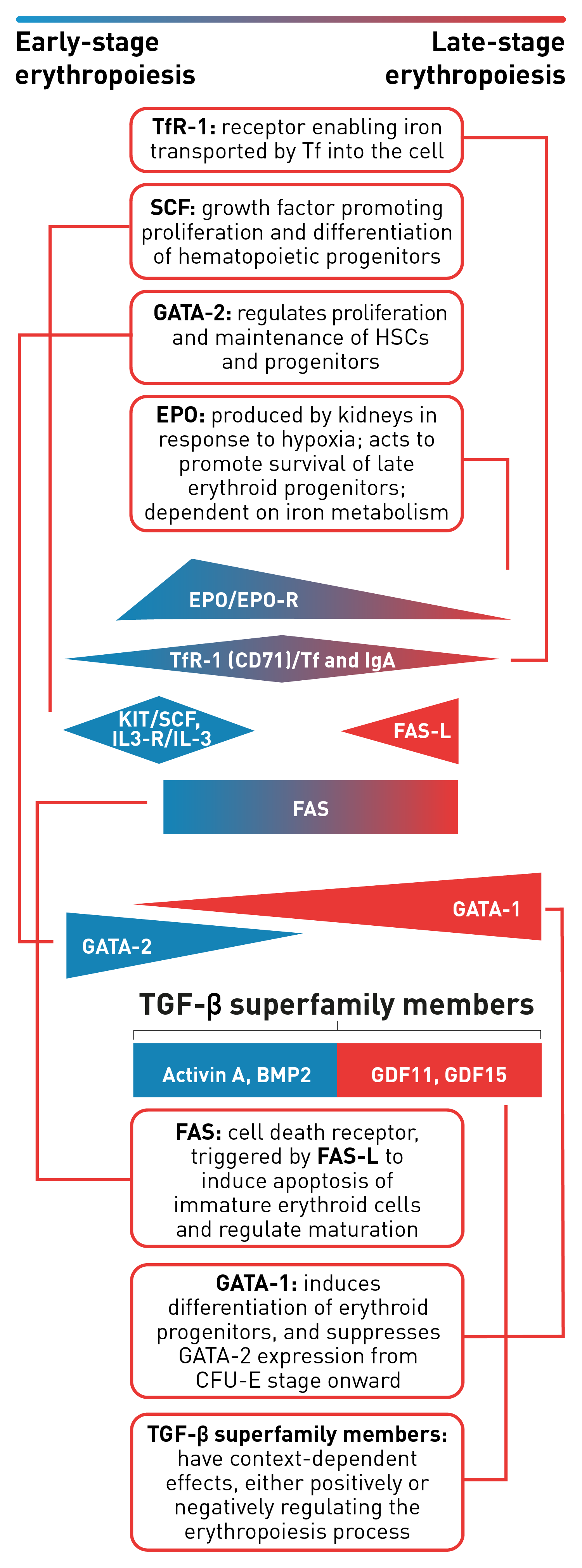
Stages of erythropoiesis
Erythropoiesis is a finely regulated, continuous process that can be conceptually divided into an early and late stage. Early-stage erythropoiesis is characterized by the proliferation of early-stage erythroid cells (progenitors), whereas late-stage erythropoiesis involves the differentiation and maturation of late-stage erythroid cells (precursors).1-3
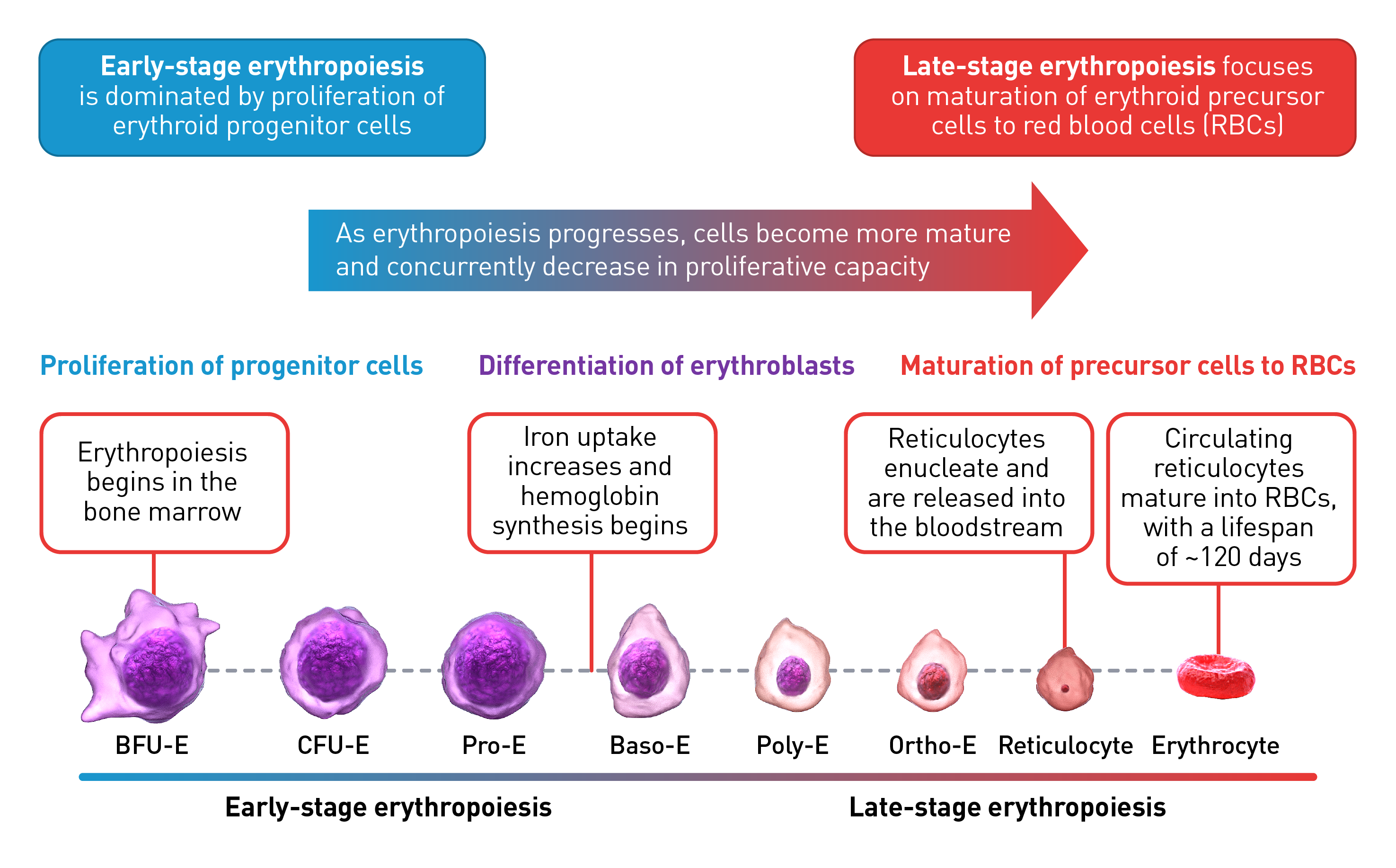
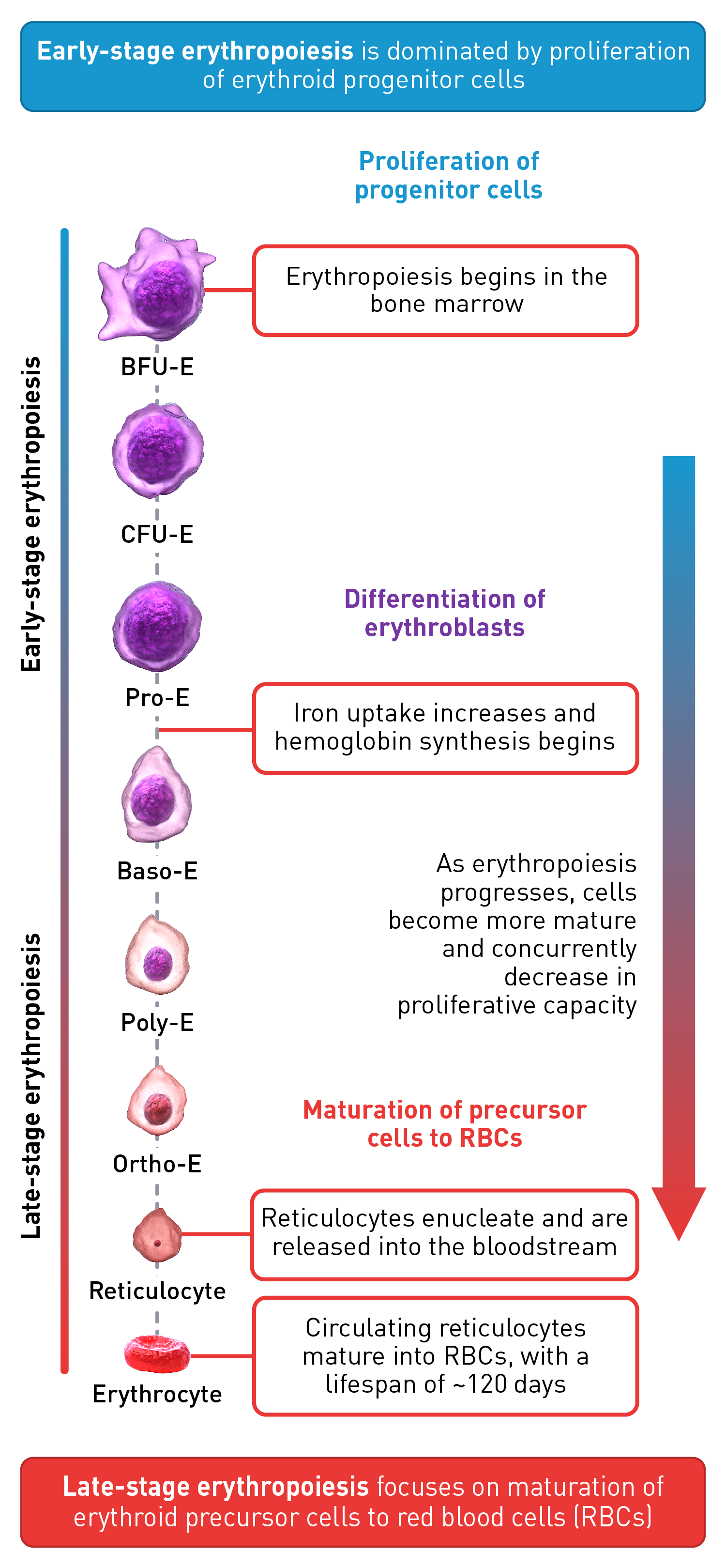
During the early stage of erythropoiesis, the proliferation of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) result in early erythroid progenitor cells. BFU-E represent the earliest progenitors committed exclusively to erythroid maturation that later differentiate into late CFU-E and Pro-E.3 Pro‑E, the earliest recognizable erythroid cells, enter terminal erythropoiesis and undergo morphological changes, such as in protein production and reduction in cell size and proliferative capacity. These changes lead to Pro-E differentiation and give rise to Baso‑E, Poly‑E and Ortho‑E, successively. At the end of this phase, erythroblasts expel their nuclei and lose all their organelles to produce mature enucleated cells, called reticulocytes.4-5 Once the nucleus is expelled, the reticulocyte is released into the bloodstream for maturation to continue and to produce fully functional, biconcave erythrocytes within 1–2 days.4
The late-stage maturation of red blood cells is an important step of erythropoiesis as it generates functional erythrocytes. Defects in this stage, known as erythroid maturation defects (EMDs), may impair the maturation process and result in ineffective erythropoiesis.6
Baso-E: Basophilic erythroid, BFU-E: Burst-forming unit-erythroid, CFU-E: Colony-forming unit-erythroid, Ortho-E: Orthochromatophilic, Poly-E: Polychromatophilic, Pro-E: Proerythroblasts, BMP2: Bone morphogenetic protein 2, EPO: Erythropoietin, EPO-R: Erythropoietin receptor, FAS-L: FAS ligand, GDF: Growth differentiation factor, IL-3: Interleukin 3, IL-3-R: Interleukin 3 receptor, IgA: Immunoglobulin A, SCF: Stem cell factor, Tf: Transferrin, TfR-1 (or CD71): Transferrin receptor, TGF: Transforming growth factor.
 This website is best viewed
This website is best viewed
using the vertical display on
your mobile device.

 3-minute video
3-minute video